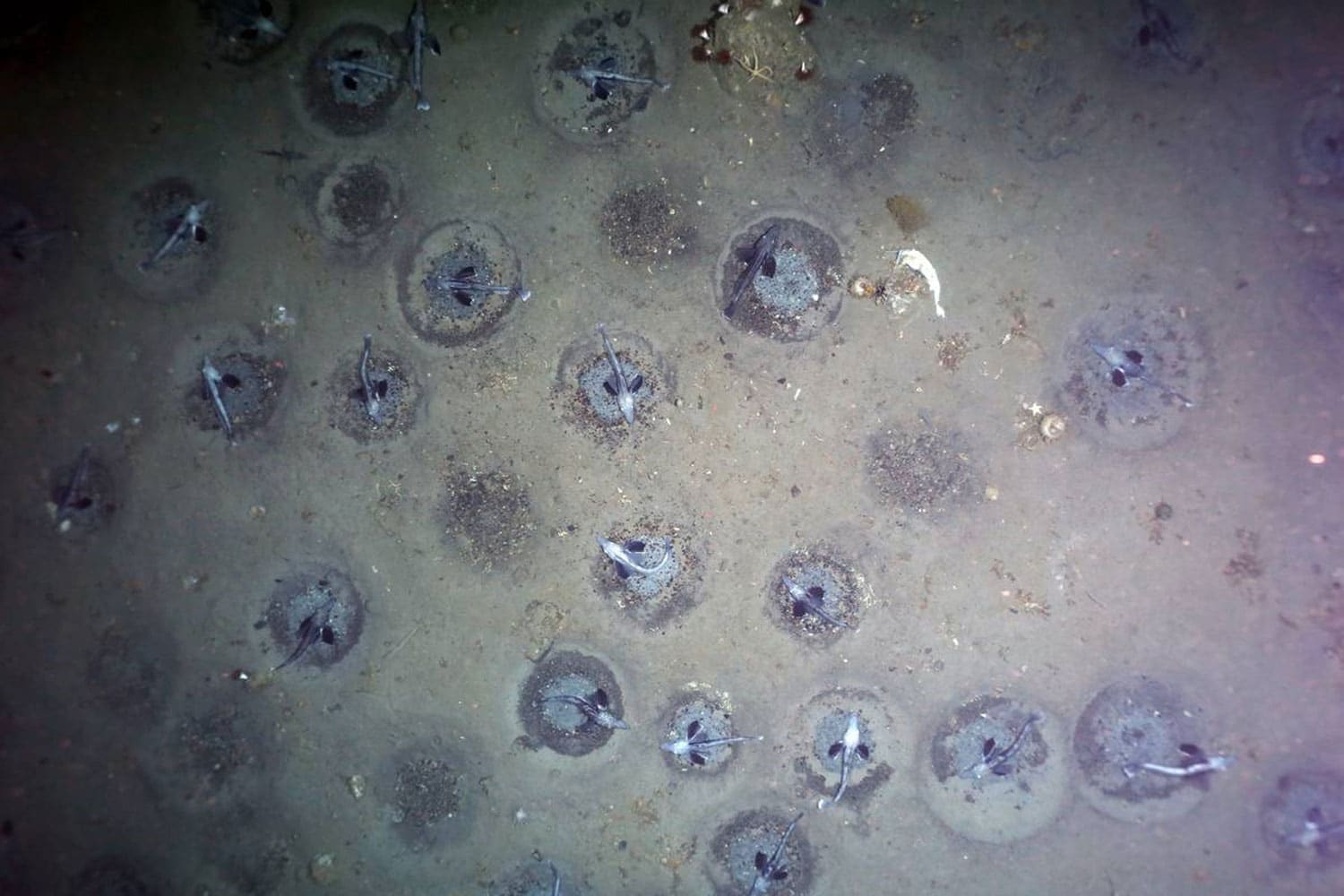
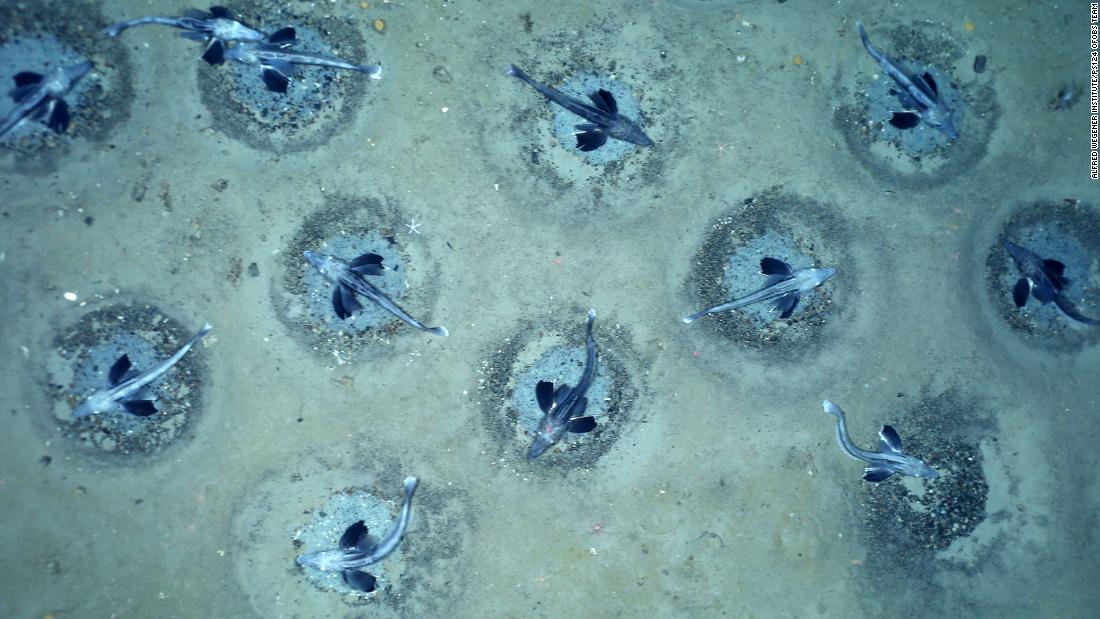
Scientific American
By John Horgan
Theories that try to explain these big metaphysical mysteries fall short, making agnosticism the only sensible stance
In my 20s, I had a friend who was brilliant, charming, Ivy-educated and rich, heir to a family fortune. I’ll call him Gallagher. He could do anything he wanted. He experimented, dabbling in neuroscience, law, philosophy and other fields. But he was so critical, so picky, that he never settled on a career. Nothing was good enough for him. He never found love for the same reason. He also disparaged his friends’ choices, so much so that he alienated us. He ended up bitter and alone. At least that’s my guess. I haven’t spoken to Gallagher in decades.
There is such a thing as being too picky, especially when it comes to things like work, love and nourishment (even the pickiest eater has to eat something). That’s the lesson I gleaned from Gallagher. But when it comes to answers to big mysteries, most of us aren’t picky enough. We settle on answers for bad reasons, for example, because our parents, priests or professors believe it. We think we need to believe something, but actually we don’t. We can, and should, decide that no answers are good enough. We should be agnostics.
Some people confuse agnosticism (not knowing) with apathy (not caring). Take Francis Collins, a geneticist who directs the National Institutes of Health. He is a devout Christian, who believes that Jesus performed miracles, died for our sins and rose from the dead. In his 2006 bestseller The Language of God, Collins calls agnosticism a “cop-out.” When I interviewed him, I told him I am an agnostic and objected to “cop-out.”
Collins apologized. “That was a put-down that should not apply to earnest agnostics who have considered the evidence and still don’t find an answer,” he said. “I was reacting to the agnosticism I see in the scientific community, which has not been arrived at by a careful examination of the evidence.” I have examined the evidence for Christianity, and I find it unconvincing. I’m not convinced by any scientific creation stories, either, such as those that depict our cosmos as a bubble in an oceanic “multiverse.”
People I admire fault me for being too skeptical. One is the late religious philosopher Huston Smith, who called me “convictionally impaired.” Another is megapundit Robert Wright, an old friend, with whom I’ve often argued about evolutionary psychology and Buddhism. Wright once asked me in exasperation, “Don’t you believe anything?” Actually, I believe lots of things, for example, that war is bad and should be abolished.
But when it comes to theories about ultimate reality, I’m with Voltaire. “Doubt is not a pleasant condition,” Voltaire said, “but certainty is an absurd one.” Doubt protects us from dogmatism, which can easily morph into fanaticism and what William James calls a “premature closing of our accounts with reality.” Below I defend agnosticism as a stance toward the existence of God, interpretations of quantum mechanics and theories of consciousness. When considering alleged answers to these three riddles, we should be as picky as my old friend Gallagher.
THE PROBLEM OF EVIL
Why do we exist? The answer, according to the major monotheistic religions, including the Catholic faith in which I was raised, is that an all-powerful, supernatural entity created us. This deity loves us, as a human father loves his children, and wants us to behave in a certain way. If we’re good, He’ll reward us. If we’re bad, He’ll punish us. (I use the pronoun “He” because most scriptures describe God as male.)
My main objection to this explanation of reality is the problem of evil. A casual glance at human history, and at the world today, reveals enormous suffering and injustice. If God loves us and is omnipotent, why is life so horrific for so many people? A standard response to this question is that God gave us free will; we can choose to be bad as well as good.
The late, great physicist Steven Weinberg, an atheist, who died in July, slaps down the free will argument in his book Dreams of a Final Theory. Noting that Nazis killed many of his relatives in the Holocaust, Weinberg asks: Did millions of Jews have to die so the Nazis could exercise their free will? That doesn’t seem fair. And what about kids who get cancer? Are we supposed to think that cancer cells have free will?
On the other hand, life isn’t always hellish. We experience love, friendship…